New Gels Could Protect Buildings During Wildfires
As climate change continues to drive hotter and drier conditions, the frequency and intensity of wildfires have escalated, extending fire seasons and amplifying their devastating impacts. In recent years, these catastrophic wildfires have not only destroyed homes and critical infrastructure but also claimed lives and livelihoods, causing extensive economic damage. The urgent need for innovative wildfire protection solutions has led researchers to explore new methods for safeguarding vulnerable areas from these destructive events.
Stanford’s Breakthrough in Wildfire Protection Gels
Researchers at Stanford University have developed a cutting-edge wildfire protection gel that offers unprecedented defense against wildfires. This new water-enhancing gel, which can be sprayed on homes and critical infrastructure, has been shown to provide longer-lasting and more effective protection compared to existing commercial gels. The findings, published on August 21 in Advanced Materials, highlight the gel’s potential to be a game-changer in wildfire protection strategies.
According to Eric Appel, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford, the new gel can be applied well in advance of a wildfire, offering extended protection even under harsh fire conditions. “Under typical wildfire conditions, current water-enhancing gels dry out in 45 minutes,” Appel explained. “We’ve developed a gel that allows for a broader application window, ensuring it remains effective when the fire arrives.”
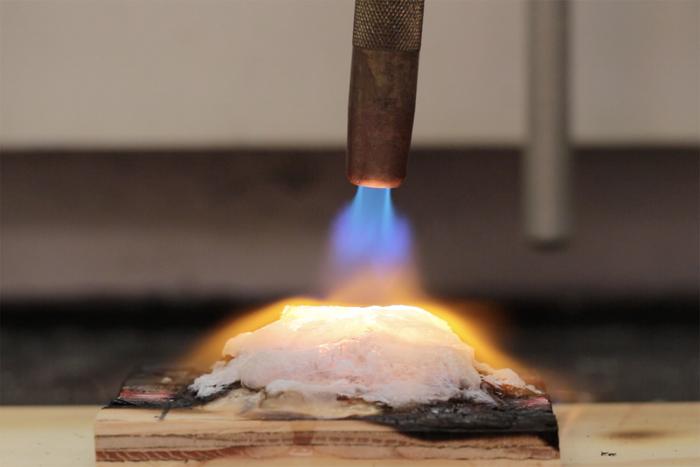

Long-Lasting Protection with Water-Enhancing Gels
Water-enhancing gels are formulated using super-absorbent polymers, similar to those found in disposable diapers. When mixed with water and applied to a building, these polymers swell into a thick, gelatinous substance that adheres to the structure’s exterior, forming a wet shield. However, the extreme conditions near a wildfire—often characterized by temperatures approaching 100 degrees Fahrenheit, high winds, and near-zero humidity—can cause even these water-locked gels to dry out quickly.
The Stanford team’s innovative gel incorporates silica particles in addition to a cellulose-based polymer, providing a secondary layer of protection. As the gel is exposed to heat, a unique transformation occurs: the soft hydrogel transitions into a robust aerogel shield. “This environmentally conscious breakthrough surpasses current commercial solutions, offering a superior and scalable defense against wildfires,” said Changxin “Lyla” Dong, the study’s lead author. The silica particles left behind after the cellulose burns off form an insulating aerogel foam, which effectively scatters heat and protects the underlying structure.
Silica Aerogels: The Ultimate Insulator
The silica aerogel formed by this process is a porous, lightweight material known for its exceptional insulating properties. Similar aerogels have been used in space applications to prevent heat transfer, making them an ideal choice for wildfire protection. The Stanford researchers tested several formulations of their new gel by applying it to plywood and exposing it to flames from a gas hand-torch, which burns at significantly higher temperatures than a typical wildfire. The most effective gel formulation protected the plywood for over seven minutes before it began to char, while a commercially available gel lasted less than 90 seconds under the same conditions.
“Our materials form this silica aerogel when exposed to fire, continuing to protect treated substrates even after all the water has evaporated,” Appel noted. “These materials can be easily washed away once the fire threat has passed.”
A Fortuitous Discovery with Lasting Impact
This innovative gel builds on Appel’s previous research in wildfire prevention. In 2019, his team used similar gels to hold fire retardants on vegetation for extended periods, helping to prevent ignition in fire-prone areas. “We’ve been working with this platform for years now,” Appel said. “This new development was somewhat serendipitous—we were curious about how these gels would behave on their own, so we tested them on wood and observed their remarkable transformation into an aerogel foam.”
Following this initial discovery, the research team spent several years refining the gel’s formulation. The result is a stable, sprayable product that adheres well to various surfaces and is easy to store. Importantly, the gels are made from non-toxic components approved for use by the U.S. Forest Service and are easily broken down by soil microbes, making them safe for both the environment and human health.
Future Applications and Potential
While the current formulation shows great promise, further optimization may be needed before these gels can be deployed on a large scale. However, Appel is optimistic about their potential. “My hope is that we can conduct pilot-scale applications and evaluations of these gels to help protect critical infrastructure when a fire comes through,” he said. The future of wildfire protection may well lie in these innovative gels, providing a new line of defense against the growing threat of wildfires.
Potential Internal Links:
- Learn more about Stanford University’s latest research initiatives.
- Explore the Advanced Materials journal for groundbreaking studies.