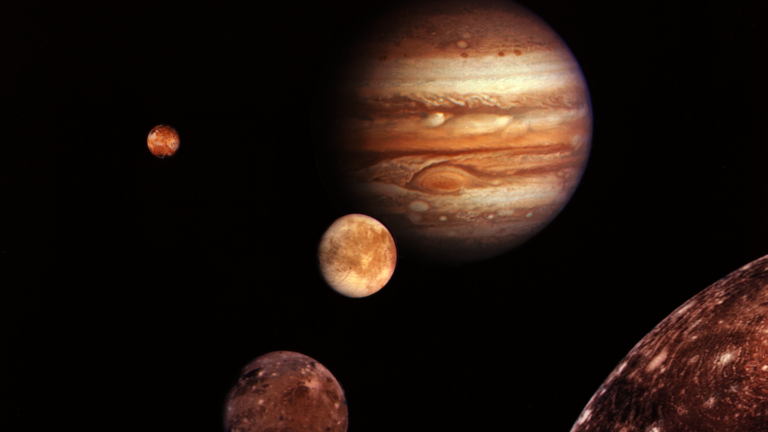
Astronomers have just made a monumental discovery—Jupiter, the fifth planet from the sun is now officially the most mooned planet in our solar system. Previously, Saturn held the title with 83 confirmed moons, but the recent discovery of 12 new moons orbiting Jupiter knocks it out of first place.
The 12 newly-discovered moons were found by a team of astronomers at Carnegie Institution for Science. Led by Scott Sheppard, they used some of the world’s most powerful telescopes to survey planets and asteroids near our solar system in search of distant objects. In March 2017, Sheppard noticed a faint object that he assumed was an asteroid or comet, but further analysis revealed it was actually a moon. After further research and observation over several months, Sheppard and his team were able to confirm twelve distinct moons orbiting Jupiter.
So why does Jupiter have so many more moons than other planets? The answer lies in its immense size and gravitational pull. All eight planets are subject to gravitational pulls from comets, asteroids, and other space debris floating around them—but because Jupiter is so large, it has more power to capture these objects into orbit around itself than any other planet does. As a result, it gathers more debris than any other planet in our solar system. These fragments then become small moons that orbit alongside larger ones like Europa and Callisto.
This news is an exciting reminder of how much we still don’t know about our universe and its secrets! Who knows what else we may find as astronomers continue to explore space? With 95 confirmed moons now orbiting Jupiter—and who knows how many more yet undiscovered—it’s safe to say that this giant planet will remain one of the most intriguing places in our universe for quite some time to come!