Recent NASA-funded studies have unearthed compelling evidence showing how climate-induced changes like melting ice, diminishing groundwater, and rising sea levels are subtly but significantly altering Earth’s rotation. This cutting-edge research utilized over 120 years of data to explore how these environmental shifts are not only nudging the planet’s spin axis but also gradually lengthening the days we experience.
Days Are Getting Longer
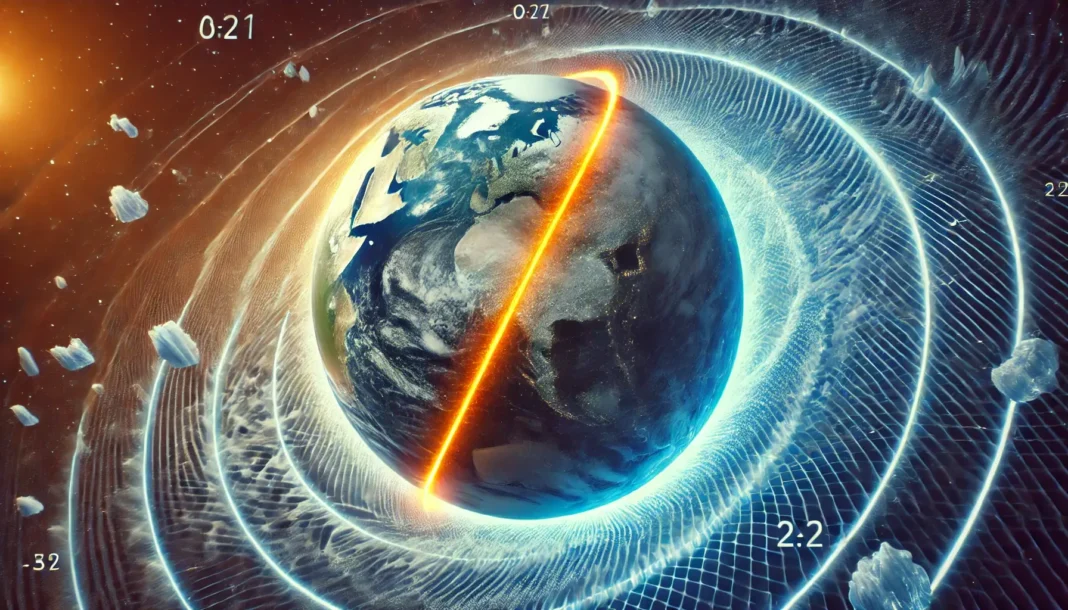
The passage of time itself is bending under the weight of climate change, with days on our planet extending incrementally. This phenomenon has been observed to accelerate recently, linked directly to the redistribution of mass around the globe due to melting ice caps and fluctuating sea levels. The spin axis of Earth has meandered by approximately 30 feet (10 meters) over the past 120 years, a direct consequence of these mass shifts.
These changes are primarily due to the increased melting of ice sheets and glaciers, which surpasses their replenishment from snowfall, and the significant reduction in groundwater levels, which is not adequately compensated by rainfall. This results in a redistribution of mass that causes Earth to wobble slightly as it spins—a phenomenon known as polar motion—which in turn impacts the planet’s rotation speed and the length of days, both of which have been measurably affected since records began in 1900.
Polar Motion and Day Length Studies
The detailed animation produced by NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio vividly illustrates how Earth’s rotation wobbles as the location of its spin axis, highlighted in orange, deviates from its geographic axis, depicted in blue. This axis represents the imaginary line between the planet’s geographic North and South poles.
In their groundbreaking research, scientists have meticulously analyzed polar motion over the last 12 decades. Their findings, recently published in Nature Geoscience, show that nearly all periodic oscillations in the axis’s position since the 1900s can be attributed to changes in groundwater, ice sheets, glaciers, and sea levels, primarily driven by natural climate cycles.
A follow-up study detailed in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences focuses on the lengthening of days, revealing that since 2000, days have been getting longer by about 1.33 milliseconds per 100 years. This increase in day length is the fastest observed pace over the past century and is largely attributed to accelerated glacial melts and the shrinking of the Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets, spurred by human-induced greenhouse gas emissions.
Technological and Natural Impacts
The necessity to account for these time changes is more critical than ever as modern technologies, such as GPS systems, rely on extremely precise timekeeping. This shift in Earth’s rotational dynamics is a testament to the profound impact human activity has had on our planet, significantly altering natural processes that have been in place for millennia.
The research utilized advanced techniques such as machine learning algorithms to dissect historical data spanning from 1900 to 2018, providing insights into the dominant influences on polar motion and day length. The studies also employed satellite observations from the GRACE mission (short for Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment) and its successor, GRACE-FO, to track changes in mass distribution across Earth’s surface.
The Future of Earth’s Rotation
Looking forward, the lengthening of days could slow by 2100 if global emissions are drastically reduced, according to the researchers. However, if emissions continue to rise, the rate of day lengthening could increase to as high as 2.62 milliseconds per century, potentially surpassing the effects of lunar tidal friction—a primary cause of Earth’s gradual deceleration over billions of years.
These findings underscore the interconnectedness of our planet’s systems and the significant, albeit subtle, changes that are occurring due to climate change. As we continue to monitor these shifts, the importance of sustainable practices and environmental stewardship becomes increasingly clear.