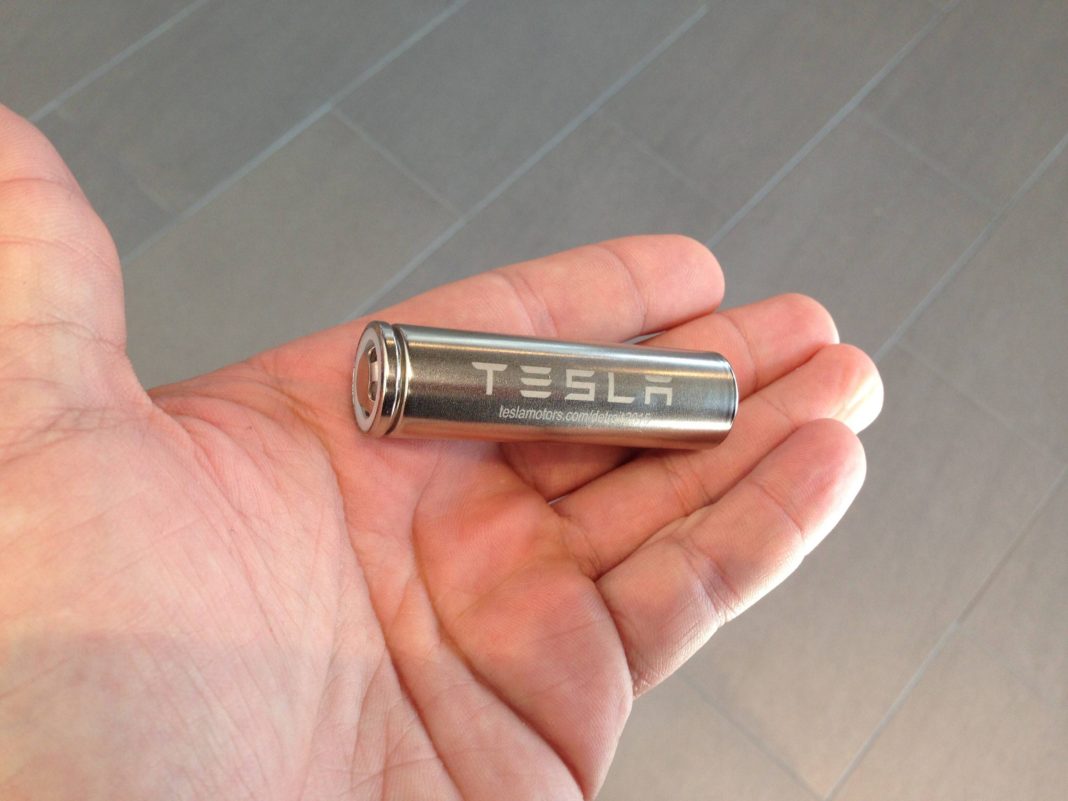
It’s arguably one of the greatest inventions to come out of the last 30 years. Since the lithium-ion battery was first introduced commercially back in the 90’s, it’s just got better and better. You will now find these batteries in a variety of devices including laptops, smartphones, and defibrillators. They are also set to help revolutionize electric cars as well as bring much-needed improvements to energy storage at grid level too.
Countries all over the world are working together on a global mission to try and combat some of the effects of climate change. One of the main ways they’re doing this is by increasing renewable energy usage. But, there’s only so much that can be added at a time, and engineers are struggling to keep up with the demand using the mix of power it gets from a variety of sources including the wind and solar. And, this is where lithium-ion batteries come in – to fill that gap.
If you’re wondering how these batteries work, here’s a brief rundown. Each battery is made up of cells that electricity flows through, with an aluminum surface on one side and copper on the other. Just like a normal battery, there’s positive and negative. While the cathode (positive electrode) is made up of lithium oxide, the anode (negative electrode) consists of a graphite layer. The battery is filled with electrolyte, which acts as a transporting medium for the flowing electricity. Finally, the permeable separator in the battery keeps the cathode and anode apart allowing it to charge efficiently.
More News To Read
- Newly Discovered Microbes, May Explain the Origin of Complex Life
- New Wearable App Detects Real Emotion in Conversation
- Without Immigrants, America Wouldn’t be America
- The Dilemma of the Black Hole Paradox – Do They Destroy Everything?
- Will This Glass Become the Future of Flexible and Lightweight Devices?