Researchers from MIT and Adobe Research have developed a technique that enables robots and machines to identify objects composed of the same materials, even when the objects have varying shapes and sizes or when lighting conditions affect their appearance. Material selection, or identifying objects made of the same material, is a challenging task for machines due to the variations in appearance caused by object shapes and lighting conditions.
The team’s approach involves training a machine-learning model using synthetic data generated by a computer that modifies 3D scenes to produce diverse images. Despite being trained on synthetic data, the model performs effectively on real-world indoor and outdoor scenes that it has never encountered before. The method can also be applied to videos, allowing the model to identify objects made from the same material throughout the entire video once the user identifies a pixel in the first frame.
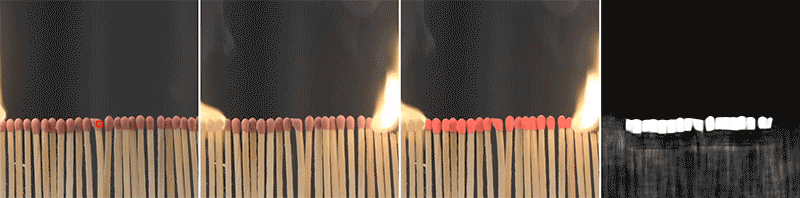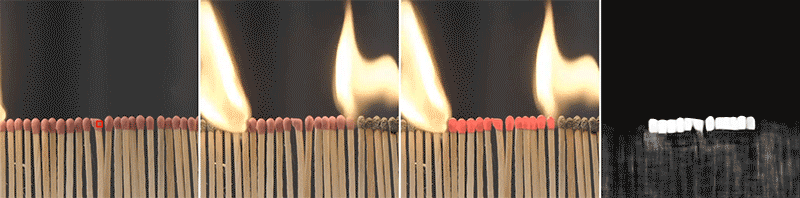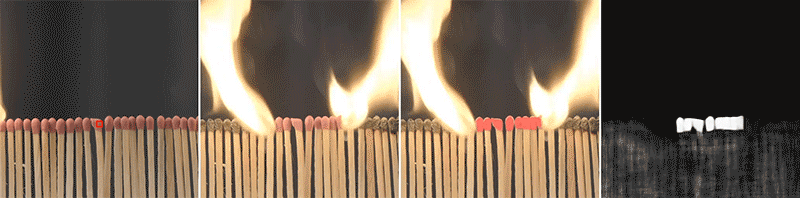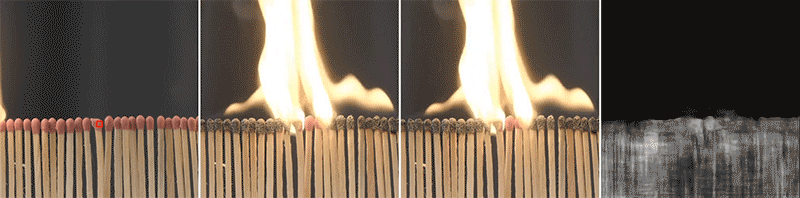
The implications of this technique extend beyond robotics and can be used in fields such as image editing, material parameter deduction in computational systems, and material-based web recommendation systems. For example, it could assist shoppers looking for clothing made from a specific type of fabric. By accurately identifying pixels representing the same material, the model can facilitate various applications that rely on material understanding.
The researchers’ method differs from existing approaches that struggle to identify all pixels representing the same material accurately. Instead of focusing on entire objects or using a predetermined set of materials, the team developed a machine-learning approach that evaluates all pixels in an image to determine the similarities between a user-selected pixel and other regions of the picture. By leveraging the visual features learned by a pre-trained computer vision model, the researchers were able to overcome the distribution shift between synthetic and real-world data.

The model converts generic visual features into material-specific features, allowing it to compute a material similarity score for every pixel in an image. When a user selects a pixel, the model determines the similarity of other pixels to the query and produces a map that ranks each pixel on a similarity scale. The user can fine-tune the results by setting a threshold and receiving a highlighted map of the image showing regions with similar materials.
During experiments, the researchers found that their model outperformed other methods in accurately predicting regions of an image with the same material, achieving approximately 92 percent accuracy compared to ground truth. In the future, they aim to improve the model’s ability to capture fine object details, which would further enhance its accuracy.
The development of this technique represents an important advancement in material recognition for computer vision algorithms. It enables machines to consider materials as a crucial aspect of scene understanding. It supports applications that benefit from precise material identification, empowering users in areas such as interior design and consumer choices.











