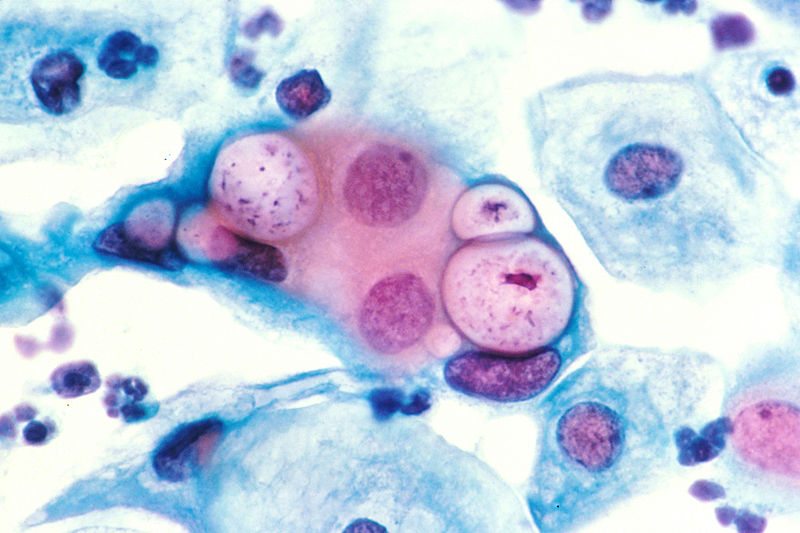
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease that affects over 90 million people a year. Quickly spread via objects, Chlamydia is parasite bacteria that cause infections within the body. It usually treated with a course of antibiotics lasting 7 or 14 days, but now scientists have discovered that proteins within the human immune system can play a huge part in the fight against Chlamydia infections. Scientists from the Federal Research and Clinical Centre of Physical-Chemical Medicine, the Koltzov Institute of Developmental Biology and the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology collaborated to carry out extensive research to prove this theory.
Reticulate bodies are the type of Chlamydia that exist inside the host cell membrane and have the ability to reproduce. Because they are constantly changing from one form to another, this gives the Chlamydia protection against most antibacterial proteins. In the search to try and fight this disease, scientists have discovered that proteins that can recognize peptidoglycan play a significant role in treating the infection. These proteins have the ability to attach to a peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharides in the cell membrane of the bacteria and cause the cell to die. PGLYRP’s use this same process to destroy Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtillis bacteria which has similar properties to the Chlamydia bacteria.
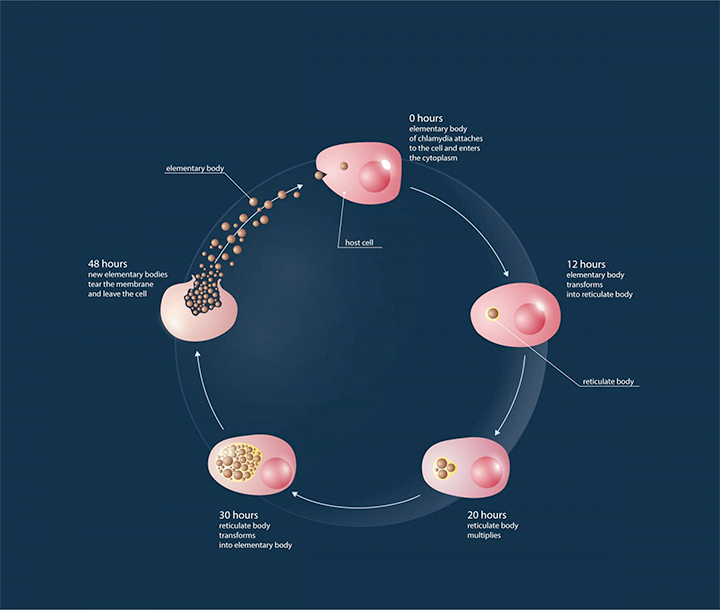
Using this as a guide, the scientists set out to complete their research and were able to prove that when PGLYRP solutions are added to human cells cultures that have been infected with Chlamydia, they have the effect of inhibiting the Chlamydia infection. The research could prove to be very valuable in the world of healthcare, and the treatment of Chlamydia and further studies are due to continue to gain an even deeper understanding of the potential targets for natural and synthetic agents, which may eventually lead to the development if antichlamydial drugs.
More News To Read