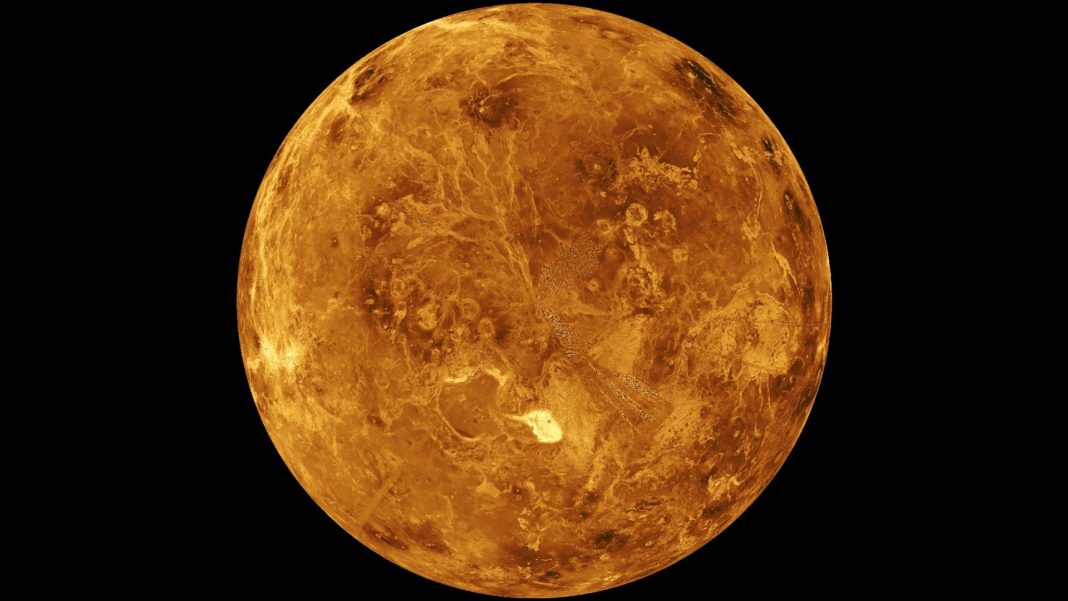
NASA’s Kepler space telescope‘s been hard at work again this month as it reveals what could possibly be a close relative to Venus. The planet is situated 219 light-years away from where it orbits a low-temperature star called Kepler-1649 around once every nine days. It has a tight orbit that causes the flux sunlight reaching the planet too much brighter than here on Earth.
Astronomers are hopeful that the discovery will provide a deeper insight into the nature of planets that exist around M dwarf stars. While M dwarf stars aren’t as bright as the sun and are redder in color, recent discoveries revealed some instances of Earth-sized planets circling M dwarf stars that would be classed as being inside the star’s habitable zone. But, that doesn’t mean to say they are like Earth. They could very well be more like Venus with thick atmospheres and scorching temperatures.
Isabel Angelo is a scientist at SETI Institute, and she says that studying planets similar to Kepler 1649b is “becoming increasingly important in order to understand the habitable zone boundaries of M dwarfs. There are several factors, like star variability and tidal effects, that make these planets different from Earth-sized planets around Sun-like stars.”
Venus may be the same size as Earth, and only about 40 percent closer to the sun, but the two planet’s atmosphere’s and temperatures differ massively. One member of the Kepler 1649b discovery team, Elisa Quintana, from the Seti Institute and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, noted, “Many people are hung up on finding other Earths. But Venus analogs are just as important. Since new telescopes coming down the pike will allow us to probe atmospheres, focusing on both Earth and Venus analogs may help decipher why, in our Solar System, one planet allows life to thrive, and one does not, despite having similar masses, comparable densities, etc.”
Related Links;
- Possible Venus twin discovered around dim star / Seti.org
- Kepler-1649b: An Exo-Venus in the Solar Neighborhood / The Astronomical Journal
More News to Read
- New Cancer Treatment May Be Having the Reverse Effect on Some Patients
- Reusable Rockets are the New ‘In Thing’ Apparently, Russian Wants Them too
- The Event Horizon Telescope Aims to Capture an Image of a Black Hole
- Can We Forecast Global Dust Storms on Mars?
- Can the New ” Light Phone ” Cure Our Smartphone Addiction?