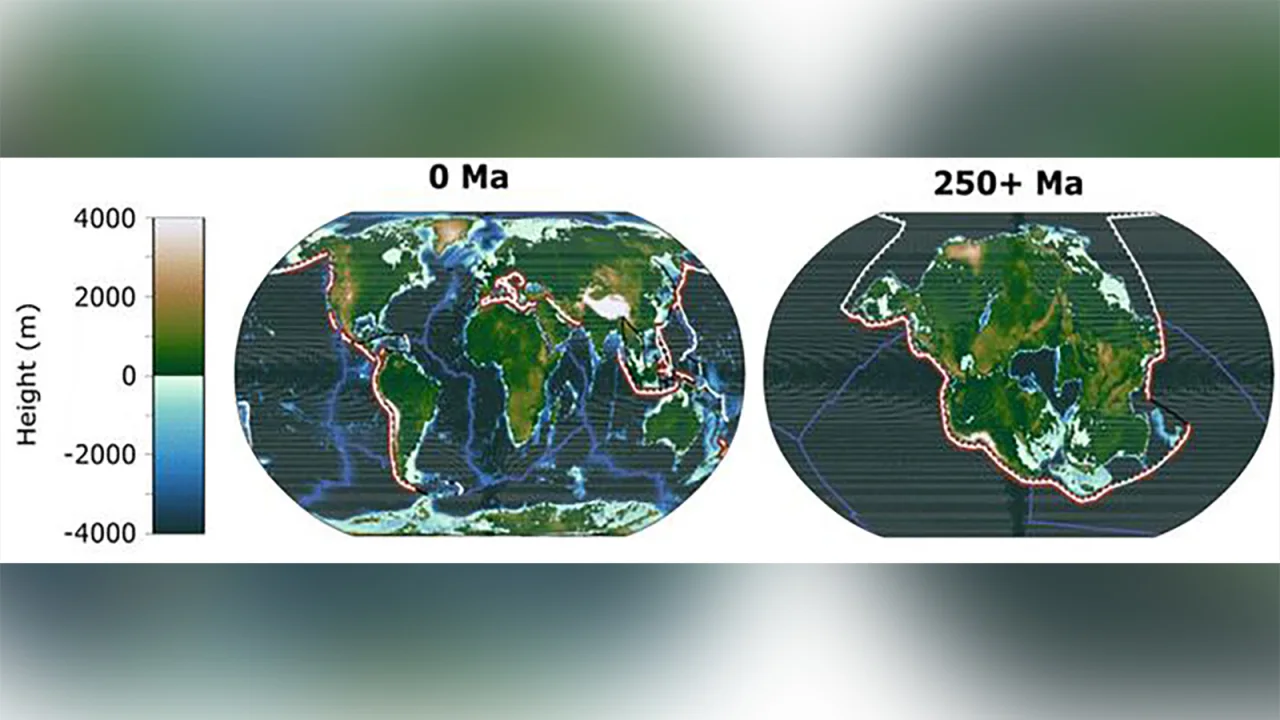
In a startling revelation, researchers have unveiled a chilling prediction for Earth’s future: the formation of a new “supercontinent” that could potentially wipe out humanity and render the planet uninhabitable within the next 250 million years. Using groundbreaking supercomputer climate models, scientists from the University of Bristol in the United Kingdom have offered a glimpse into a future where climate extremes intensify following the merger of the world’s continents into a single entity known as Pangea Ultima.
The Impact of Pangea Ultima: A Harsh Reality
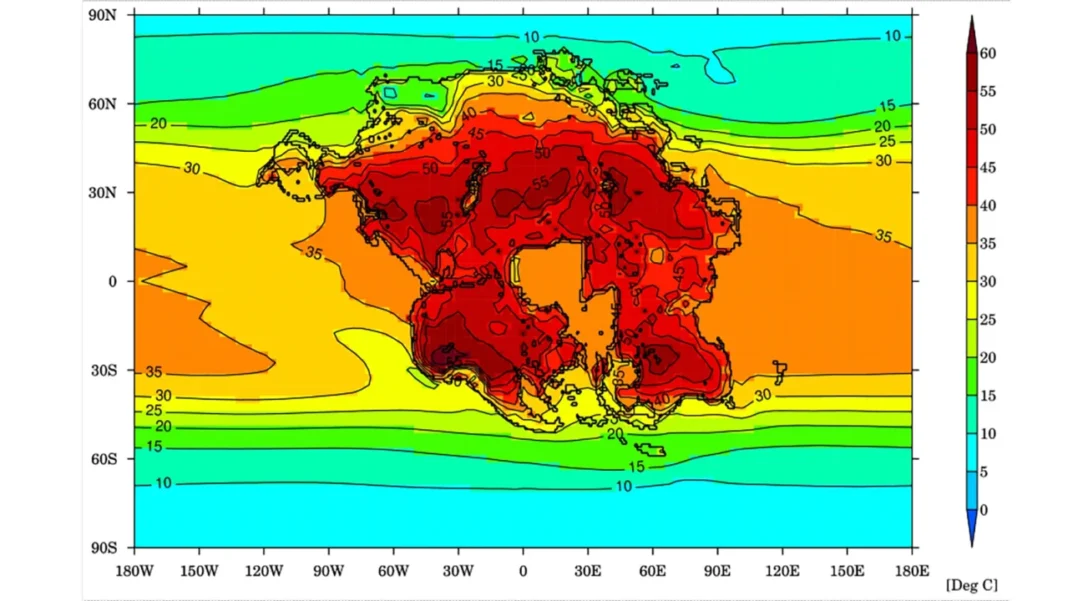
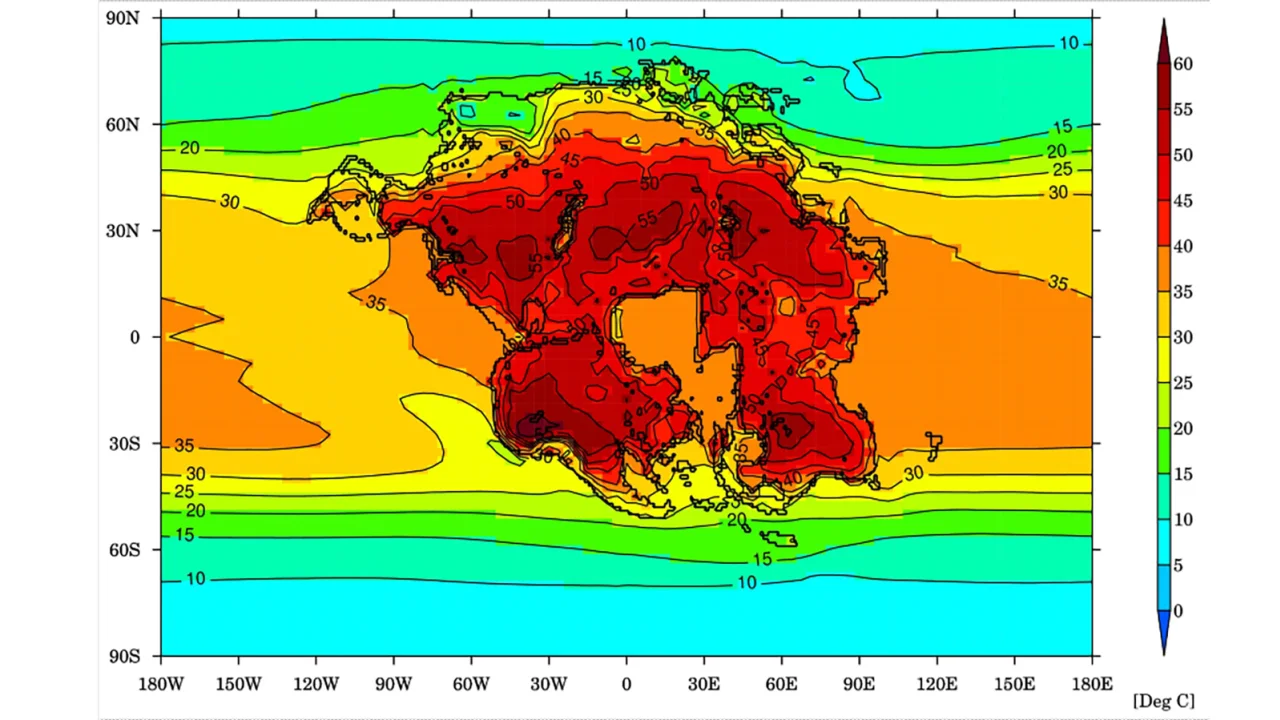
According to their findings, the consequences of Pangea Ultima’s formation would be catastrophic for humans and mammals. The supercontinent’s climate would become scorching, arid, and virtually uninhabitable for species ill-equipped to withstand prolonged exposure to extreme heat. To reach this conclusion, researchers simulated temperature fluctuations, wind patterns, rainfall trends, and humidity levels for the supercontinent. Additionally, they factored in models of tectonic plate movements, ocean chemistry, and biological interactions to estimate carbon dioxide levels.
The results were alarming. Pangea Ultima’s emergence would not only lead to an increase in volcanic eruptions, releasing more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and heating the planet, but it would also cause the sun to emit greater amounts of energy, further contributing to Earth’s warming. The combination of these factors, as Alexander Farnsworth, senior research associate at the University of Bristol, pointed out, would create a devastating “triple whammy”: continentality effect, intensified solar radiation, and elevated CO2 levels.
The consequences of this dire scenario include widespread temperatures ranging from 40 to 50 degrees Celsius (104 to 122 degrees Fahrenheit), along with extreme daily temperature fluctuations, all exacerbated by high humidity levels. In such conditions, humans and many other species would be unable to cool their bodies through sweat, ultimately leading to their demise. The elevated heat would also result in a stark scarcity of food and water sources for mammals.
The Grim Projections: Land Habitable for Mammals
While predictions about the distant future carry significant uncertainties, the outlook appears bleak. Researchers estimate that only 8% to 16% of the supercontinent’s land would remain habitable for mammals. Moreover, the report suggests that if humans continue to burn fossil fuels, carbon dioxide levels could double their current levels, hastening the dire consequences.
However, this grim vision of Earth’s future serves as a stark reminder not to become complacent about addressing the current climate crisis. Human-caused climate change is already causing millions of deaths globally each year. Eunice Lo, a research fellow at the University of Bristol, emphasized the urgency of reaching net-zero emissions promptly to combat today’s climate challenges.
The Urgency of Combating Climate Change
The consequences of climate change are not limited to the distant future. A UN-backed report from last year warned that climate change is on track to transform life on Earth, jeopardizing billions of people and countless species unless global warming is substantially slowed. The goal of limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels remains crucial, with the need to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels becoming increasingly pressing.
The potential formation of a new “supercontinent” paints a grim picture of Earth’s future, but it also serves as a powerful reminder of the urgency to address the ongoing climate crisis. As we look ahead to the next 250 million years, our actions today can shape the destiny of our planet.
1. What are the 2 supercontinents? Currently, Earth has two recognized supercontinents. The first is Eurasia, which is a combination of the continents of Europe and Asia. The second is Afro-Eurasia, which includes Africa, Europe, and Asia. These supercontinents are the result of the Earth’s ever-changing geology and the movement of tectonic plates.
2. What are the 3 supercontinents? Throughout Earth’s long history, there have been three primary supercontinents. The first is Rodinia, which existed around 1.3 billion to 750 million years ago. The second is Pangaea, which formed around 335 million years ago and began to break apart roughly 175 million years ago, leading to the current continents. The most recent supercontinent is Pangea Ultima, a hypothetical future supercontinent that is predicted to form in around 250 million years based on geological models.
3. What was the first supercontinent? The first recognized supercontinent in Earth’s history was Rodinia. It existed during the Precambrian era, approximately 1.3 billion to 750 million years ago. Rodinia was a vast landmass that predated the more famous supercontinent Pangaea and played a significant role in shaping the planet’s geological history.
4. What is Earth’s supercontinent? As of the present day, Earth does not have a single supercontinent. Instead, it has multiple continents that are in constant motion due to the process of plate tectonics. However, the most recent supercontinent in Earth’s history was Pangaea, which existed from around 335 million years ago until it began breaking apart approximately 175 million years ago, leading to the continents we know today. Currently, we are not in a supercontinent phase, but geological models predict the potential formation of a future supercontinent called Pangea Ultima in about 250 million years.