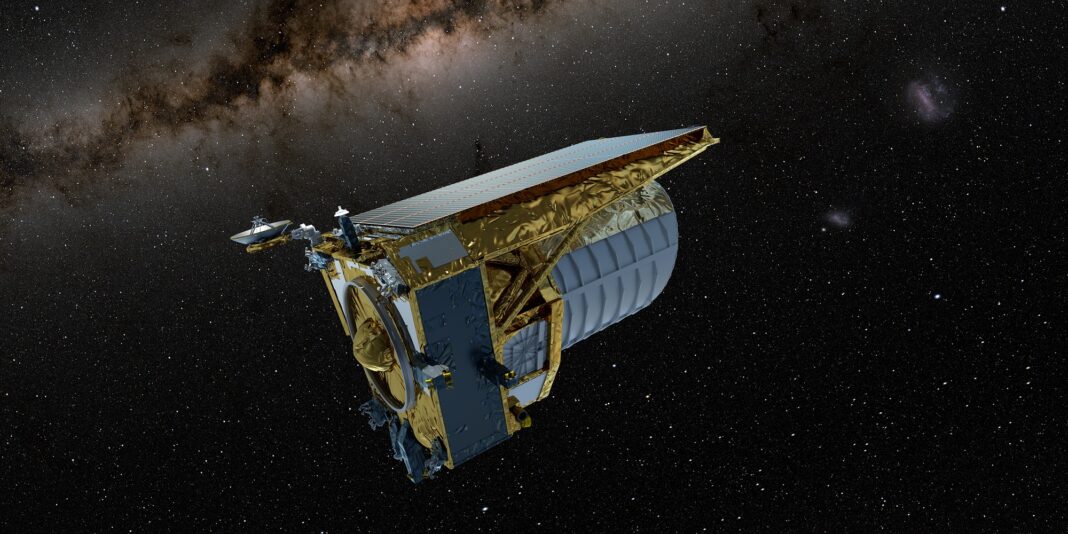
On a momentous day, July 1st, the ESA’s Euclid space telescope embarked on its extraordinary journey, departing from Cape Canaveral in Florida. This groundbreaking astrophysics mission, known as Euclid, is poised to traverse the vast expanse of space over the next six years, focusing its gaze on one-third of the celestial sphere from its perch at the Earth-Sun L2 Lagrange Point. Armed with state-of-the-art instruments, Euclid aims to unlock the secrets of the universe, delving into the enigmatic realms of Dark Matter and Dark Energy (DM & DE) that have long perplexed astronomers and cosmologists.
The momentous launch occurred at precisely 11:12 AM EST (08:12 AM PST) atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. Within a mere few minutes, the second stage gracefully separated, paving the way for Euclid’s cosmic odyssey. At around 3 minutes and 37 seconds into the flight, the payload fairings gracefully detached, a testament to the flawless execution of the mission. Within a span of forty-five minutes, the vigilant ground controllers received confirmation that Euclid had successfully disengaged from the second stage, firmly establishing its position in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). Over the course of the next two weeks, Euclid will meticulously deploy its sunshield and gradually reach its operating temperature, preparing itself for the momentous journey to L2 on July 29th, precisely four weeks after the initial launch.
Euclid, armed with its remarkable 600-megapixel camera, near-infrared spectrometer, and a photometer designed to measure the redshift of galaxies, aspires to forge an unparalleled 3D map of the Universe. This ambitious endeavor will encompass a mind-boggling observation of billions of galaxies, stretching their spectral footprints to an astonishing distance of 10 billion light-years. By charting the vast cosmic web that spans billions of light-years, Euclid aims to shed light on the profound mysteries surrounding Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the evolution of our universe.
The crux of Euclid’s mission lies in deciphering the cosmic saga of expansion that has unfolded over the past 10 billion years, an era that coincides with the dominion of Dark Energy. During this epoch, the Universe experienced an accelerated expansion, defying conventional wisdom and challenging the existing understanding of gravity’s role. By mapping the vast cosmic structure and its evolution through time, Euclid aims to unravel the intricate interplay between gravity, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy. These fundamental forces bear significant relevance to the ongoing “Crisis in Cosmology,” encompassing the enigmatic rotational curves of galaxies that defy the conventional explanations based on visible matter alone. Scientists first observed this anomaly in the 1960s, sparking the notion that galaxies consist of a significant portion of invisible, or “dark,” matter. The enigma deepened in the 1990s when the existence of Dark Energy was speculated upon, primarily catalyzed by the groundbreaking observations of the Hubble Space Telescope and its Deep Fields campaigns.
As humanity’s gaze traverses the vast cosmic ocean, astronomers and cosmologists have observed a startling revelation. The cosmic expansion, instead of gradually decelerating, has been accelerating for the past four billion years. This perplexing conundrum, coupled with the enduring enigma of Dark Matter, challenges our understanding of gravity as described by the theory of General Relativity. It beckons us to consider the possibility of an unknown force counteracting gravity on cosmic scales. Based on the prevailing cosmological model, the Lambda Cold Dark Matter (LCDM) model, cosmologists estimate that Dark Energy constitutes a staggering 72% of the mass-energy density
Dark matter and dark energy are two mysterious phenomena that have perplexed scientists for years. Dark matter refers to an invisible substance that does not interact with light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation, making it undetectable through conventional means. However, its presence is inferred through its gravitational effects on visible matter. It is believed to make up a significant portion of the total mass in the universe and plays a crucial role in the formation and structure of galaxies.
On the other hand, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe. Unlike dark matter, dark energy is not associated with the presence of mass. Its nature and composition remain largely unknown, posing a significant challenge to cosmologists trying to comprehend the fundamental forces at work in the cosmos.
The mission of the Euclid space telescope, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), is to investigate the nature of dark matter and dark energy, two major cosmic mysteries. Euclid will conduct a comprehensive survey of the sky, observing billions of galaxies over a period of six years. By mapping the large-scale structure of the universe and studying the way it has evolved over billions of years, Euclid aims to provide invaluable insights into the properties and distribution of dark matter and dark energy. It will create the most extensive 3D map of the universe to date, helping scientists better understand the fundamental forces shaping our cosmos.
The European Space Agency (ESA) is involved in numerous missions aimed at advancing our understanding of the universe. Apart from the Euclid mission, some notable ESA missions include:
- The Planck mission: Launched in 2009, the Planck space observatory mapped the cosmic microwave background radiation, providing detailed insights into the early universe and the formation of cosmic structures.
- The Rosetta mission: This historic mission successfully landed a spacecraft on a comet in 2014, providing invaluable data about comets and their composition. It also included the Philae lander, which marked the first-ever soft landing on a comet’s surface.
- The Gaia mission: Launched in 2013, the Gaia space observatory is creating a precise 3D map of the Milky Way galaxy, charting the positions, distances, and motions of over a billion stars.
The Euclid Space Telescope will primarily observe galaxies to a distance of 10 billion light-years. It will map the large-scale cosmic structure, charting how the universe has expanded over the past 10 billion years. Euclid’s observations will help scientists understand the role of gravity, dark matter, and dark energy in shaping the cosmos. By studying the redshift of galaxies and analyzing their distribution, Euclid aims to shed light on the mysteries of the universe’s evolution and provide valuable insights into the nature of dark matter and dark energy.
The NASA-ESA mission refers to collaborative missions between NASA (the National Aeronautics and Space Administration) and ESA (the European Space Agency). These joint missions bring together the expertise, resources, and scientific contributions of both agencies to undertake ambitious scientific endeavors. Examples of NASA-ESA missions include the Hubble Space Telescope, which was launched by NASA but involved collaboration with ESA for scientific instruments and support, and the James Webb Space Telescope, which is a joint endeavor between NASA, ESA, and the Canadian Space Agency. These collaborative missions aim to advance our understanding of the universe, explore distant cosmic phenomena, and push the boundaries of scientific knowledge.