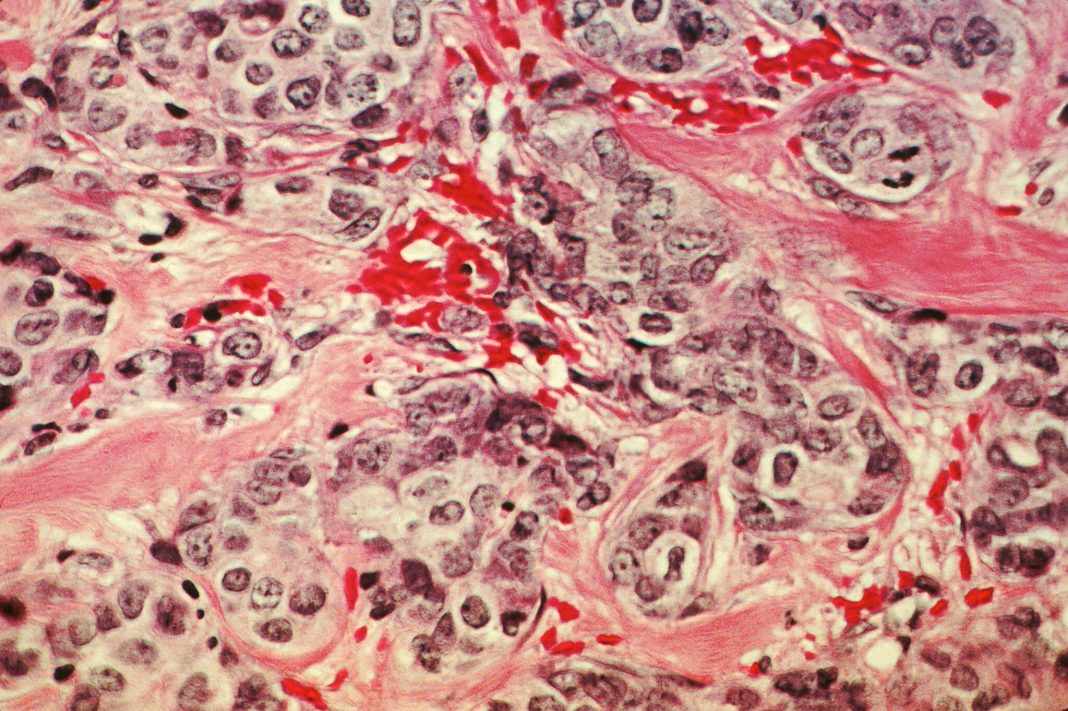
A study out of the University of Pennsylvania has found that some of the most aggressive forms of cancer mimic virus in order to spread, grow, and resist treatment. The results of the study were published this week in the journal Cell. Now that the mechanism that aids in the process is understood, researchers can start focusing on the treatments that might stop the action and prevent the spread of certain cancers like triple-negative breast cancer and BRCA1.
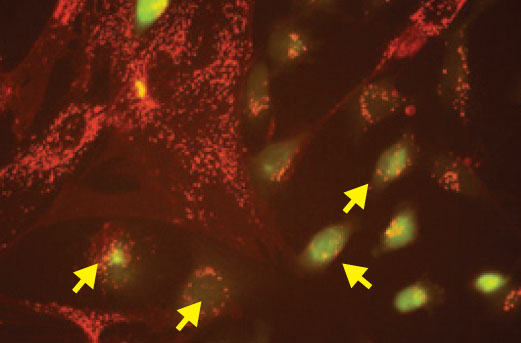
Inside of cancer tumors are also regular cells like certain immune cells and fibroblasts. It is these cells that cancer exploits to help it spread through the body. Additionally, it is these immune cells that release high levels of ISGs, or interferon-stimulated genes, which are normally only present in the case of viral attacks. The ISGs are indicators that the cancer tumors are imitating viruses.
The Perelman School of Medicine researchers found that the cells of aggressive cancers stimulate the body’s fibroblasts to release small sacs, called exosomes, filled with a certain form of RNA called RN7SLI.
RN7SLI differs from other RNA because its tip looks similar to the RNA found in viruses causing cancer to react as if there were a viral infection and increasing inflammation.
Lead author Andy J. Minn, MD, Ph.D., and professor of Radiation Oncology explains the importance of these findings: “If the end remains covered, breast cancer cells wouldn’t treat these exosomes like a virus, making them less likely to progress and more likely to respond to treatment. On the other hand, if the end is always exposed, cells would react as if they are infected with a virus all the time.”
Previous work by Minn and his team suggests that treatments which block NOTCH pathways might stop cancer’s instruction to the fibroblasts. When used in mice suffering from triple-negative breast cancer, NOTCH treatments were found to be effective.
More News to Read
- Mathematical Algorithms Reveal New Information About Aggressive Breast Cancer
- New AI Finds Recipes Using only Pics of Food
- Will Spintronics Soon Replace Silicon in Next Phase Computers and Phones?
- Breakthrough IBM Z Mainframe Promises to Stop Data Theft
- Quantum Data can be Secure even When Remote Accessed with Traditional Computers