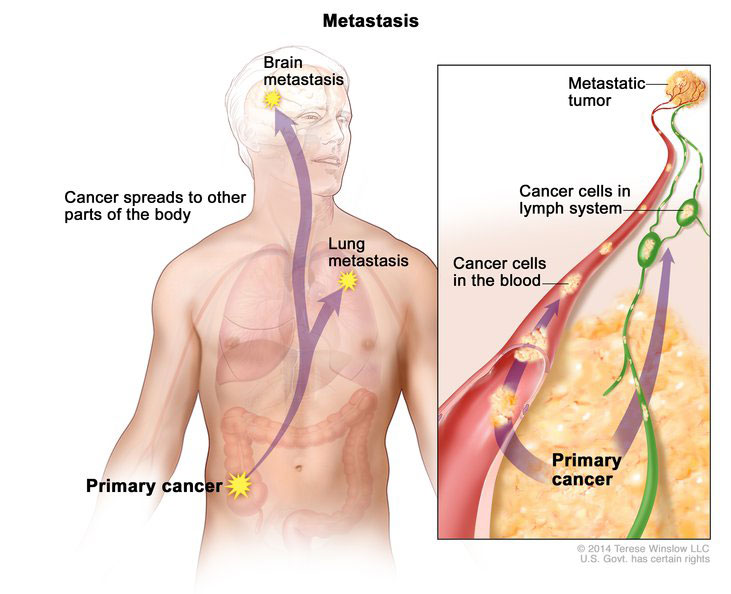
In cancer patients, metastasis in the principal cause of death and currently there is no effective treatment to stop it. Hopefully, the results of recent research can hinder or even completely stop the spread of cancer cells throughout the body.
When cancer metastasizes, it travels through the body, penetrating healthy organs, and causing tumors in previously unaffected tissues. The latest research focuses on stopping a cancer cell’s ability to migrate, effectively stopping the metastasizing process in its tracks.
Cancer cells are able to move due to a set of fibers that aid in their migration. Mostafa El-Sayad, Julius Brown Chair and Regents Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Georgia Tech, and his team removed and disabled these fibers using a newly developed technique. Their findings are published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The fibers that move cancer cells around are long, thin protrusions called filopodia. They are extensions of fibers found around the edge of cells, called lamellipodia.
These tiny faux legs occur in many cells and help to get them where they need to go. However, in cancer cells, both filopodia and lamellipodia are created excessively making them quicker movers. Using tiny rods made of gold nanoparticles, called nanorods, the researchers were able to destroy the legs.
The use of nanotechnology allowed scientists to decrease the size of materials to a billionth of a meter where they take on different and new physical and chemical characteristics. Then they were coated in RGD peptides in order to adhere to a protein called integrin, and the nanorods were injected locally by researchers.
“The targeted nanorods tied up the integrin and blocked its functions, so it could not keep guiding the cytoskeleton to overproduce lamellipodia and filopodia,” explains co-author Dr. Yan Tang.
By binding the nanorods to the integrin, metastasizing was delayed. Additionally, the treatment does not appear to injure healthy cells the way toxic radiation or chemotherapy can, which can lead to dramatically better treatment experience for cancer patients.
“There are certain, specific integrins that are overproduced in cancerous cells,” explains Moustafa Ali, another of the study’s authors. “And you don’t find them so much in healthy cells.”
For the next stage, the research team used a near-infrared laser to heat the nanoparticles of gold, forcefully stopping malignant cancer from metastasizing.
“The light was not absorbed by the cells, but the gold nanorods absorbed it, and as a result, they heated up and partially melted cancer cells they are connected with, mangling lamellipodia and filopodia,” says Moustafa Ali.
For the sake of the experiment, the cancer cells were not killed. To complete the study Prof. El-Sayed and team needed to observe if the cancer cells would migrate and thus required living cells. However, this same heating technique could be used to kill off the cancer cells completely, in theory.
Previous experiments conducted on mice, using the same methods, found no gold toxicity for 15 months after treatment.
Currently, the laser can only penetrate tissue up to 5 centimeters thick, but deeper injections of the golden nanorods can still slow the spread of cancer.
In the future, Prof. El-Sayad hopes this leads to cancer therapies to treat “head, neck, breast, and skin cancers with direct, local nanorod injections combined with the low-power near-infrared laser.”
More News to Read
- What Does it Take to Build the Super Collider?
- According to a New Study, Early Life Stress Can Change Genes in Brain
- Stunning View of Aurora Borealis from ISS in new NASA video
- Imagine Being Able to Explore the Brain Like a Website
- Quantum Computers Made Even More Powerful with New microchip generating ‘Qudits.’