A new type of planetary object has been proposed this month which scientists are calling a synestia. While this doughnut-shaped object may have been present in the Universe for quite some time, and given rise to the Earth, scientists have only just uncovered it. It’s thought to form when one planet bashes into another and may soon appear in textbooks everywhere if made official by the astronomy community.
“We show that rocky planets are vaporized multiple times during their formation, and are likely to form synestias”, report Simon Lock from Harvard University and Sarah Stewart from UC Davis. “The different structures of hot, rotating planets change our understanding of multiple aspects of planet formation, including the origin of our Moon.”
The most widely accepted theory of how our own planet formed is that a few billion years ago an object similar to the size of Mars formed in the Solar System in the path of a protoplanet that was soon to become Earth. The two finally collided in what’s typically known as the ‘giant impact’ sending a great deal of debris into space, some of which went off to form the Moon. The remainder was Earth, which is said to have formed officially about 4.5 billion years ago.
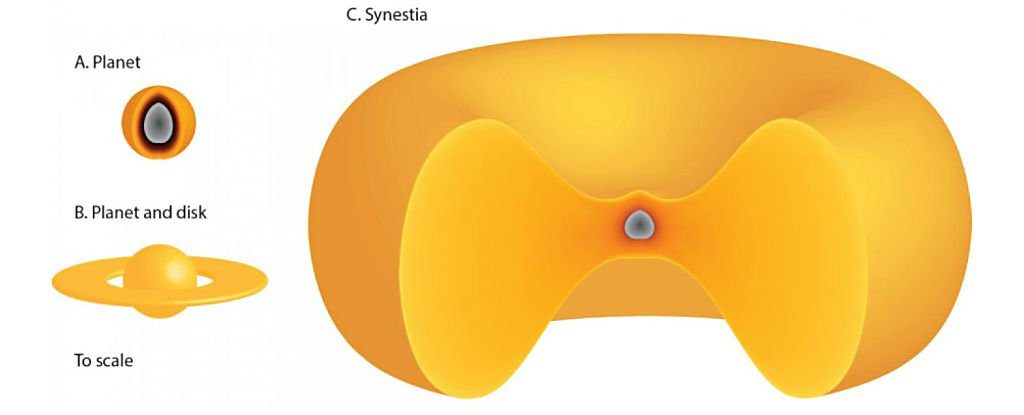
But, what if this collision was actually a little more complicated than that? Lock and Stewart have been investigating the formation of our planet in its earliest moments and they’ve suggested a couple of outcomes, one of which no one has yet to think of. The first outcome is one that is commonly known and involves a disc or debris encircling our Sun which eventually clumped together to form larger orbiting objects. These objects would get so big that eventually they would collide and rocky planets such as Earth, Mars, and Venus would form as a result.
If one of the colliding objects was small the new planet would get bombarded with meteorites, but if it was big, the shattered remains could end up orbiting the planet for a while, like Saturn’s rings, before eventually getting consumed by it. What Lock and Stewart proposed in their model were what would happen if one large, hot object slammed into a similar spinning mass at a night angular momentum. The results were that these actions would produce synestias.
Synestias are haloes of vaporized rock that spin around a molten core that survives for a couple hundred years on average. These have a volume much larger than the two colliding objects and hold no solids nor liquids on its surface. “We looked at the statistics of giant impacts, and we found that they can form a completely new structure,” Stewart said. From their research, the team proposed that after spending a century or so in this state, the synestia would have lost so much heat that it would transform back into a solid. They’ve also suggested that most planets that are around today were in fact synestias at some point in time. If this is confirmed later as true, it could help reveal how the Moon really formed. Until then, scientists will just have to continue gathering evidence and we’ll just have to wait and see what comes of it all.
Related Links;
- A New Type of Planetary Object Has Been Proposed – And It Could Explain Earth’s Origin
- The structure of terrestrial bodies: Impact heating, corotation limits, and synestias
More News to Read
- Why Not Use the Moon as A Gas Station to Get to Mars?
- Researchers Discover How to Store Information In Chemicals
- Are These Mini Spherical Reactors the Answer to Fusion Energy’s Problems?
- Scientists Subject Quantum Entanglement to Extreme Levels of Acceleration
- New Monster Mars Rover Looks a Little Scary











