There are estimated to be around 100 million black holes or more within the Milky Way galaxy. Even though only a few have been identified so far, researchers have found them to have masses ranging from 5 to 10 times than of the sun. However now, using the ASTE Telescope in Chile and the 45-meter Radio Telescope at Japan’s Nobeyama Radio Observatory a new black hole has been discovered that is estimated to be around 36 times that of the sun! That’s a huge black hole!
This monstrous black hole was discovered accidentally as researchers were observing molecular clouds around W44, a supernova remnant located about 10,000 light-years away from us here on Earth. One of the molecular clouds the team observed was named “Bullet” as it was moving so fast through space, averaging at over 50 miles per second. Masaya Yamada, a graduate student at Keio University in Japan said, “Most of the Bullet has an expanding motion with a speed of 50 km/s, but the tip of the Bullet has a speed of 120 km/s. Its kinetic energy is a few tens of times larger than that injected by the W44 supernova. It seems impossible to generate such an energetic cloud under ordinary environments.”
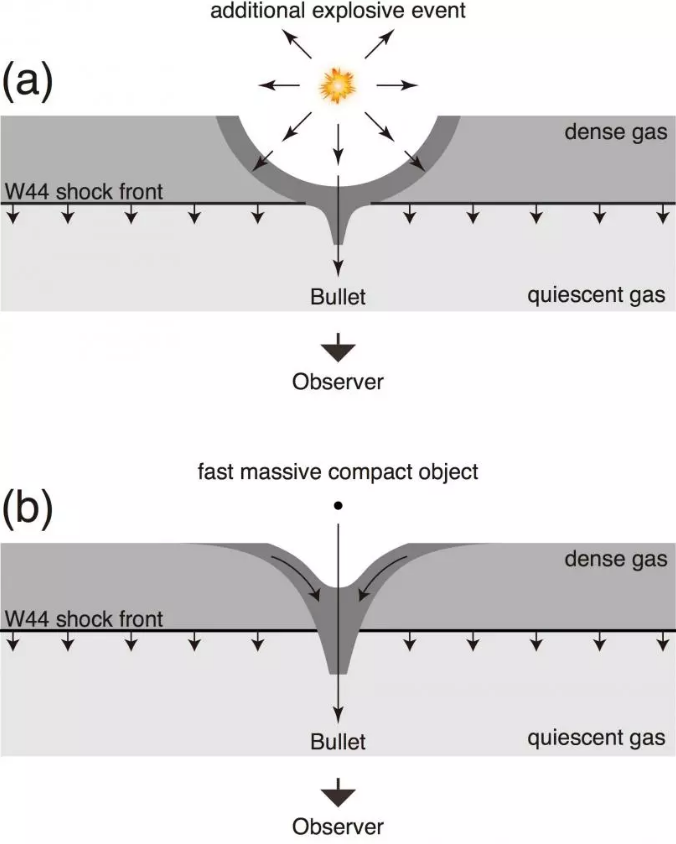
However, the researchers have come up with two possible ideas as to how the cloud was created, both of which involved studying the motion of gas inside. The first idea involves the gas shell of supernova remnant going by a black hole, while the other involves a black hole hurtling through a dense gas cloud, then dragged along by the black hole’s gravitational force. The researchers are pleased with their findings and are hopeful that their methods used to make the discovery will be used in the future to reveal more stray black holes that we don’t realize are there.
More News To Read
- The Ins and Outs of the Lithium-Ion Battery
- Is it Even Possible to Calculate When the Universe Began?
- Scientists Discover Gatekeeper Cells May Hold the Key to Beating Alzheimer’s
- Parents Turn to Machine Learning to Keep Track of Kids
- Understand Easier How Engines Work By Seeing the Explosion Inside a See Through Engine











